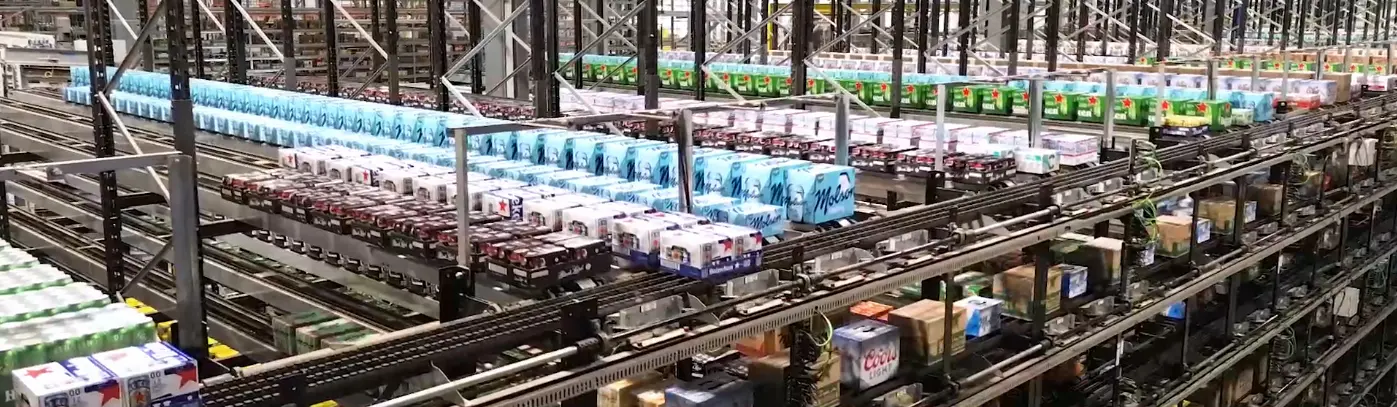
In the ever-evolving world of automation and warehousing, three technologies stand out for their efficiency and innovation in case storage and retrieval (ASRS): crane-based mini-load ASRS, case shuttle ASRS, and motorized conveyor ASRS. Each of these systems has unique features and benefits, making them suitable for different applications. Let’s dive into the specifics of each technology and compare their strengths and weaknesses.
Crane-Based Mini-Load ASRS
Crane-based mini-load ASRS utilizes cranes to pick and place items in storage locations. This technology is known for its flexibility, as it can handle items of varying sizes. While it offers a lower storage density compared to case shuttle ASRS and motorized conveyor ASRS, it has the advantage of accepting heavier products.
One drawback of this system is the interdependence between throughput and storage capacity; if more throughput is required, additional storage capacity must be added, and vice versa. Typically, a crane-based mini-load ASRS can achieve around 100-120 ins and outs per hour per crane.
Case Shuttle ASRS
Case shuttle ASRS employs shuttles, which are small wheeled vehicles that travel in aisles to pick and place products in storage locations. This technology boasts a higher storage density than crane-based mini-load ASRS but falls short compared to motorized conveyor ASRS.
One of its key advantages is the ability to increase throughput without necessarily expanding storage capacity, making it highly effective for operations where throughput is the dominant requirement. Depending on the number of shuttles in the system, case shuttle ASRS can achieve around 1000 ins and outs per hour per aisle.
Motorized Conveyor ASRS
Motorized conveyor ASRS relies on conveyors to store and retrieve products. It offers the highest storage density among the three technologies because no aisles are required. Products can be added on one end and released on the other end, or they can be added and released from the same end.
Motorized conveyor ASRS can handle around 1400 ins and outs per hour per level. This solution is therefore mainly valuable for fast moving products. However, to increase storage capacity, additional buffer lanes per level are needed, and to boost throughput, more levels must be added. This system also has more limitations on product sizes compared to the other technologies due to its configuration: product length must comply with the physical limitations of the buffer lanes and supporting structure.
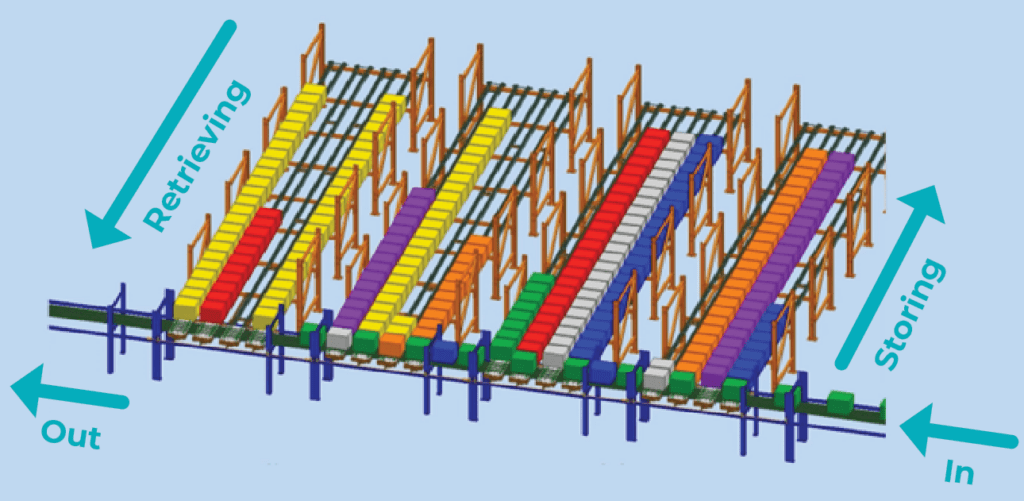
Here’s a visual example of NūMove’s motorized conveyor ASRS called InnoPick. Only one level is shown for clarity.
Summary of the Pros & Cons of each ASRS Technology
| Mini-Load ASRS | Case Shuttle ASRS | Motorized Conveyor ASRS | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pros |
– Flexible in handling items of varying sizes, shapes and weights – Ideal for small parts in industries like electronics, pharmaceuticals, and e-commerce |
– High storage density with multi-deep product storage – Suitable for bulk storage in industries like food and beverage, cold storage, and manufacturing – Uses autonomous vehicles or shuttles for efficient handling of heavier, bulkier goods |
– Highest storage density (no aisles) – Highest throughput – Ideal for fast-moving products |
| Cons |
– Lower storage density compared to Case Shuttle ASRS – Not as efficient for bulk storage – Throughput tied to storage capacity |
– Less flexible in handling items of varying sizes and shapes – Higher initial setup cost – Requires more space for shuttle lanes – Lower density than motorized conveyor |
– Limited product size compatibility – Scaling requires more buffer lanes or levels |
Conclusion
Each automatic storage and retrieval system has its own set of strengths and weaknesses. Crane-based mini-load ASRS is flexible and can handle heavier products but offers lower storage density and speed. Case shuttle ASRS provides higher storage density and throughput but requires careful planning to optimize the number of shuttles. Motorized conveyor ASRS excels in storage density and throughput but has limitations on product sizes and requires additional levels or buffer lanes to scale. Understanding the specific needs of your operation is crucial in selecting the right ASRS system. Whether you prioritize flexibility, throughput, or storage density, there is a solution that can meet your requirements and enhance your warehousing efficiency.
